This progressive and debilitating disease can lead to stroke, heart failure, and Alzheimer’s disease, and can double your risk of death. Afib takes a physical toll, an emotional toll, and a financial toll on those who are living with it—not just the patient, but the family, too.
Although atrial fibrillation itself usually isn’t life-threatening, it is a serious medical condition that sometimes requires emergency treatment.
It can lead to complications.
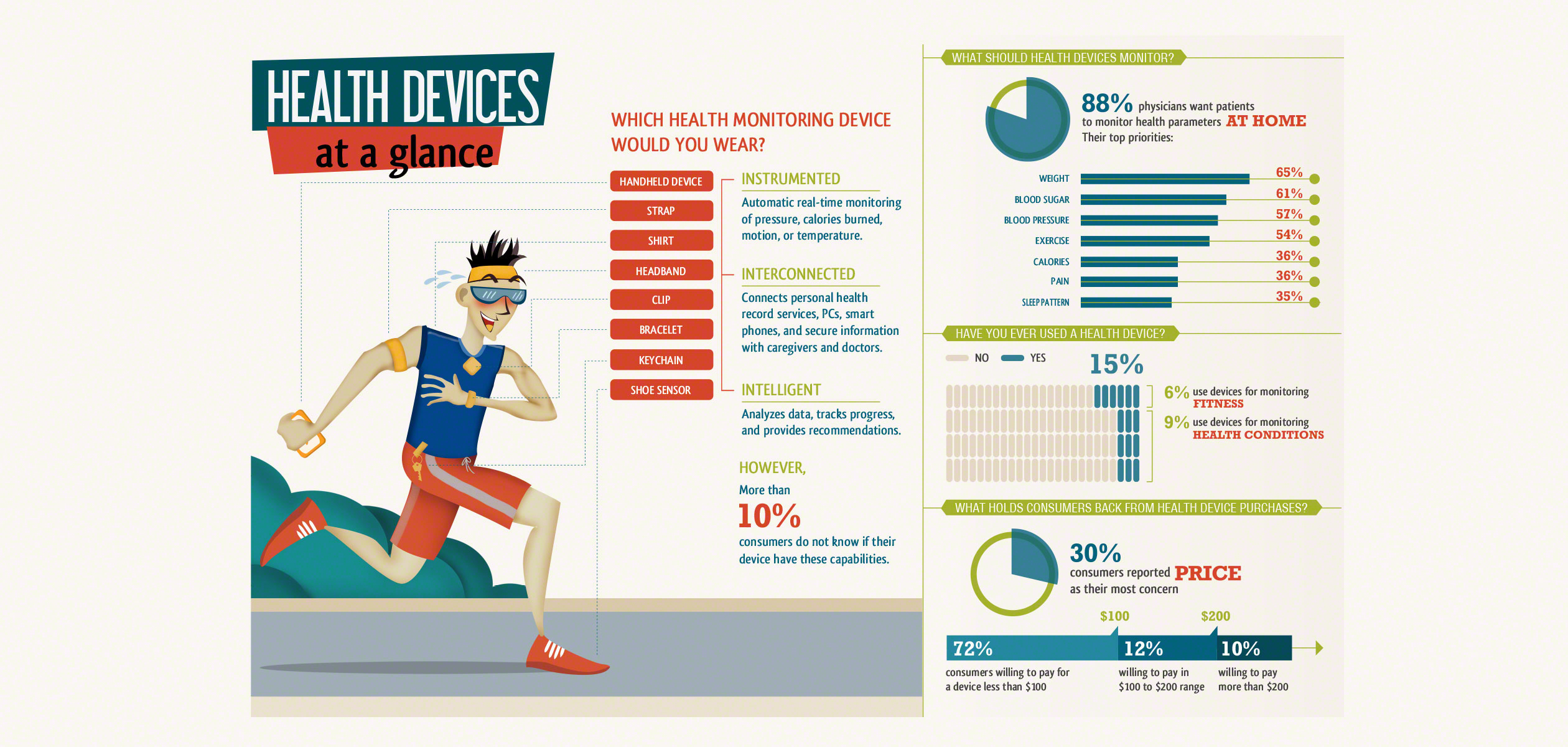
Symptoms of A Fib
• Skipping, fluttering,or quivering of heartbeat
• Heart beating too hard or fast
• Dizziness or lightheadedness
• Confusion
• Shortness of breath
• Chest pain or pressure
• Tired when resting or when active
• Swelling of feet, ankles,and legs
• Feeling anxious
Here is a short video Do you know what Atrial Fibrillation feels like?
What Causes Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (AF) occurs if the heart’s electrical signals don’t travel through the heart in a normal way. Instead, they become very rapid and disorganized. With atrial fibrillation (AFib),the electrical signals of the heart are abnormal.
• The top and bottom parts of the heart don’t work together as they should
• The heart beats very fast and irregularly
• As a result,blood is not properly pumped to the bottom part of the heart and the rest of the body
Damage to the heart’s electrical system causes AF. The damage most often is the result of other conditions that affect the health of the heart, such as high blood pressure and coronary heart disease.

Understanding the Electrical Problem in Atrial Fibrillation
In AF, the heart’s electrical signals don’t begin in the SA node. Instead, they begin in another part of the atria or in the nearby pulmonary veins. The signals don’t travel normally. They may spread throughout the atria in a rapid, disorganized way. This can cause the atria to fibrillate.
The faulty signals flood the AV node with electrical impulses. As a result, the ventricles also begin to beat very fast. However, the AV node can’t send the signals to the ventricles as fast as they arrive. So, even though the ventricles are beating faster than normal, they aren’t beating as fast as the atria.
Thus, the atria and ventricles no longer beat in a coordinated way. This creates a fast and irregular heart rhythm. In AF, the ventricles may beat 100 to 175 times a minute, in contrast to the normal rate of 60 to 100 beats a minute.
If this happens, blood isn’t pumped into the ventricles as well as it should be. Also, the amount of blood pumped out of the ventricles to the body is based on the random atrial beats.
The body may get rapid, small amounts of blood and occasional larger amounts of blood. The amount will depend on how much blood has flowed from the atria to the ventricles with each beat.
Most of the symptoms of AF are related to how fast the heart is beating. If medicines or age slow the heart rate, the symptoms are minimized.
AF may be brief, with symptoms that come and go and end on their own. Or, the condition may be ongoing and require treatment. Sometimes AF is permanent, and medicines or other treatments can’t restore a normal heart rhythm.
Major Risk Factors
A good question to ask your healthcare provider is what is the cause of my AFib?
Atrial Fibrillation is more common in people who have:
- High Blood Pressure
- Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
- Heart Failure
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Structural heart defects, such as mitral valve prolaps
- Pericarditis; a condition in which the membrane, or sac, around your heart is inflamed
- Congenital Heart Defects
- Sick sinus syndrome (a condition in which the heart’s electrical signals don’t fire properly and the heart rate slows down; sometimes the heart will switch back and forth between a slow rate and a fast rate)
AF also is more common in people who are having heart attack or who have just had surgery. The risk of AF increases as you age. Inflammation also is thought to play a role in causing AF. Drinking large amounts of alcohol, especially binge drinking, raises your risk. Even modest amounts of alcohol can trigger AF in some people. Sometimes, the cause of AF is unknown.

Treatment Goals
• Slow heart rate
• Regain normal heartbeat
• Treat causes
• Lower risk of stroke and heart failure
Warning Signs of Stroke
• Numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg ,especially on ONE side
• Confusion
• Difficulty speaking or understanding
• Trouble seeing in one or both eyes
• Trouble walking or with balance
• Dizziness
• Severe headache
Warning Signs of Heart Failure
• Shortness of breath
• Trouble doing usual activities
• Difficulty breathing when lying flat
• Weight gain
• Swelling in legs, ankles, or feet
Treatment options
Heart Procedures
Cardioversion is done two ways: An electrical procedure, in which your heart is given low-energy shocks to trigger a normal rhythm. You’re temporarily put to sleep before the shocks are given. This type of cardioversion is done in a hospital as an outpatient procedure. “Outpatient” means you can go home after the procedure is done.
Cardioversion through use of medicines. Using medicines to correct arrhythmias also is a form of cardioversion. This type of cardioversion usually is done in a hospital, but it also can be done at home or in a doctor’s office. It is known as a rhythm controller
During catheter ablation, a series of catheters (thin, flexible wires) are put into a blood vessel in your arm, groin (upper thigh), or neck. The wires are guided into your heart through the blood vessel.
A special machine sends energy to your heart through one of the catheters. The energy destroys small areas of heart tissue where abnormal heartbeats may cause an arrhythmia to start.
Catheter ablation often involves radiofrequency (RF) energy. This type of energy uses radio waves to produce heat that destroys the heart tissue. Studies have shown that RF energy works well and is safe.
Lifestyle changes
- Do I need to change my eating habits?
- Should I change my activity level?
- What else can I do to lower my risk?
- Stopping smoking
- Limiting/avoiding alcohol
- Limiting/avoiding caffeine
Resources:
Living with Atrial Fibrillation patient educational materials
Learn about Atrial Fibrillation here
A heart away from stroke documentary Discovery Channel explores the connection between atrial fibrillation and stroke – in order for patients to learn about the importance of stroke prevention
Sources:
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/index.htm
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/atrial-fibrillation/DS00291
http://www.stopafib.org/